Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an interface to establish communication between devices and a host controller (usually personal computer). Nowdays USB has replaced a variety of earlier PC interfaces (such as RS-232 serial, parallel port, and even FireWire). Due to the ability to supply power to the preipheral devices USB is often used as a power charger for portable devices. An USB system architecture consists of a host controller, a USB ports, and multiple connected devices. Additional USB hubs may be included allowing branching into a tree structure with up to five tier levels. USB can connect computer peripherals such as mice, keyboards, digital cameras, PDA, mobile phones, printers, personal media players, Media Transfer Protocol (MTP) devices, flash drives, GPS, Network Adapters, and external hard drives. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB interface aimed to remove the need for adding expansion cards into the computer's PCI or PCI-Express bus, and improve plug-and-play capabilities by allowing devices to be hot swapped or added to the system without rebooting the computer. There are several types of USB connectors. The connector mounted on the host or device is called the receptacle, and the connector attached to the cable is called the plug. The original USB specification detailed Standard-A and Standard-B plugs and receptacles. Nowdays there are 7 USB connectors known: Standard-A, Standard-B, Mini-A, Mini-B , Micro-A, Micro-AB, Micro-B, Type-C. Mini-USB pinout and Micro-USB pinout are slightly different: standard USB uses 4 pins while Mini-USB and Micro-USB uses 5 pins in connector. The additional pin is used as an attached device presence indicator. USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires: two for power (+5v & GND) and two for differential data signals (labelled as D+ and D- in pinout). NRZI (Non Return to Zero Invert) encoding scheme used to send data with a sync field to synchronise the host and receiver clocks. In USB data cable Data+ and Data- signals are transmitted on a twisted pair. No termination needed. Half-duplex differential signaling helps to combat the effects of electromagnetic noise on longer lines. Contrary to popular belief, D+ and D- operate together; they are not separate simplex connections. USB 2.0 provides for a maximum cable length of 5 meters for devices running at Hi Speed. Univeral serial bus supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer modes. There are some major USB versions known nowdays: USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 shares same connector pinout, USB 3.0 pinout and USB Type C features new connectors with their own pinouts. An USB device must indicate its speed by pulling either the D+ or D- line high to 3.3 volts. These pull up resistors at the device end will also be used by the host or hub to detect the presence of a device connected to its port. Without a pull up resistor, USB assumes there is nothing connected to the bus. In order to help user to identify maximum speed of device, a USB device often specifies its speed on its cover with one of the USB special marketing logos. When the new device first plugs in, the host enumerates it and loads the device driver necessary to run it. The loading of the appropriate driver is done using a PID/VID (Product ID/Vendor ID) combination supplied by attached hardware. The USB host controllers has their own specifications: UHCI (Universal Host Controller Interface), OHCI (Open Host Controller Interface) with USB 1.1, EHCI (Enhanced Host Controller Interface) is used with USB 2.0. The USB connector provides a single 5 volt wire from which connected USB devices may power themselves. A given segment of the bus is specified to deliver up to 500 mA. This is often enough to power several devices, although this budget must be shared among all devices downstream of an unpowered hub. A bus-powered device may use as much of that power as allowed by the port it is plugged into. Bus-powered hubs can continue to distribute the bus provided power to connected devices but the USB specification only allows for a single level of bus-powered devices from a bus-powered hub. This disallows connection of a bus-powered hub to another bus-powered hub. Many hubs include external power supplies which will power devices connected through them without taking power from the bus. Devices that need more than 500 mA or higher than 5 volts must provide their own power. When USB devices (including hubs) are first connected they are interrogated by the host controller, which enquires of each their maximum power requirements. However, seems that any load connected to USB port may be treated by operating system as device. The host operating system typically keeps track of the power requirements of the USB network and may warn the computer's operator when a given segment requires more power than is available and may shut down devices in order to keep power consumption within the available resource. To recognize Battery Charging, a dedicated charging port places a resistance not exceeding 200 Ω across the D+ and D− terminals. Dedicated charger mode: A simple USB charger should incorporate 200 Ohm resistor between D+ and D- wires (sometimes shortcircuit D+ and D- together is enough). The device will then not attempt to transmit or receive data, but can draw up to 1.8A, if the supply can provide it. Supplied voltage by a host or a powered hub ports is between 4.75 V and 5.25 V. Maximum voltage drop for bus-powered hubs is 0.35 V from its host or hub to the hubs output port. All hubs and functions must be able to send configuration data at 4.4 V, but only low-power functions need to be working at this voltage. Normal operational voltage for functions is minimum 4.75 V. Shield should only be connected to Ground at the host. No device should connect Shield to Ground. Shielded:
Data: 28 AWG twisted
Power: 28 AWG - 20 AWG non-twisted Non-shielded:
Data: 28 AWG non-twisted
Power: 28 AWG - 20 AWG non-twisted
pinouts.ru Правильная распиновка штекера и гнезда Micro-USB разъема для подключения питания и зарядки мобильного телефона или планшета. Назначение контактов микро-USB разъема — гнезда и штекера Разъем USB (Universal Serial Bus) – это последовательная шина универсального назначения, наиболее распространённый проводной способ подсоединения внешних устройств к компьютеру. Данный разъем позволяет организовывать обмен данными между компьютером и видеокамерой, карт-ридером, MP3 — плеером, внешним жестким диском, смартфоном. Кроме того, по нему поступает напряжение питания 5 вольт для зарядки аккумулятора носимых гаджетов. Так как практически все современные литиевые батареи имеют рабочее напряжение 3,7 В, то идущие по Микро-ЮСБ 5 В подходят для восполнения энергии отлично. Правда не напрямую к АКБ, а через преобразователь зарядного устройства. Радует, что цоколёвка разъёма одинаковая у всех производителей смартфонов — Самсунг, LG, Huaway и другие. Таким образом зарядное-адаптер 220 В от одного телефона, чаще всего подходит для заряда другого без изменения цоколёвки. Обратите внимание: Разъём micro содержит 5 контактов. В разъёмах типа «B» четвёртый контакт не используется. В разъёмах типа «A» четвёртый контакт замкнут с GND (минус). А для GND — пятый контакт. 2shemi.ru USB (универсальная последовательная шина) – Интерфейс передачи данных USB сегодня распространён повсеместно, используется практически во всех устройствах телефонах, ПК, МФУ, магнитофонов и в других устройствах применяются как для передачи данных так и для зарядки батарей телефона. Существует большое количество разновидностей типов разъёмов ЮСБ. Все они показаны ниже. Тип А — активное, питающее устройство (компьютер, хост). Тип B — пассивное, подключаемое устройство (принтер, сканер) USB является последовательная шина. Он использует 4 экранированных провода: два для питания (+ 5v & GND) и два для дифференциальных сигналов данных (помечены как D + и D-). USB micro используется с 2011 г. в телефонах, Mp3 и в других устройствах. Micro — это более новая разновидность разъема mini. У него есть преимущество в соединение разъемов, разъем соединен плотно со штекером и обеспечивает плотное соединения. Читайте также Распиновка штекера 3.5 мм (наушники). prohelps.ruРаспиновка USB штекера. Usb схема
USB распиновка и описание @ pinouts.ru
Pin
Name
Cable color
Description
1
VCC
Red
+5 VDC
2
D-
White
Data -
3
D+
Green
Data +
4
GND
Black
Ground
USB connectors
USB pinout signals
USB transfer modes
USB interfaces specifications.
USB 1.0 - Low Speed or Full Speed
USB 2.0 - High Speed
USB 3.0 - SuperSpeed
USB powered devices
USB power usage:
Specification
Current
Voltage
Power (max)
Low-power device
100 mA
5 V
0.50 W
Low-power SuperSpeed (USB 3.0) device
150 mA
5 V
0.75 W
High-power device
500 mA
5 V
2.5 W
High-power SuperSpeed (USB 3.0) device
900 mA
5 V
4.5 W
Battery Charging (BC) 1.2
1.5 A
5 V
7.5 W
Type-C
1.5 A
5 V
7.5 W
3 A
5 V
15 W
Power Delivery 2.0 Micro-USB
3 A
20 V
60 W
Power Delivery 2.0 Type-A/B/C
5 A
20 V
100 W
USB voltage:
USB cable shielding:
USB cable wires:
Power Gauge
Max length
28
0.81 m
26
1.31 m
24
2.08 m
22
3.33 m
20
5.00 m
Распиновка микро USB разъема | 2 Схемы

Схема распиновки

Заряд батареи через Микро-ЮСБ

Различие Micro-USB A и B

Схема соединения Micro-USB с обычным USB

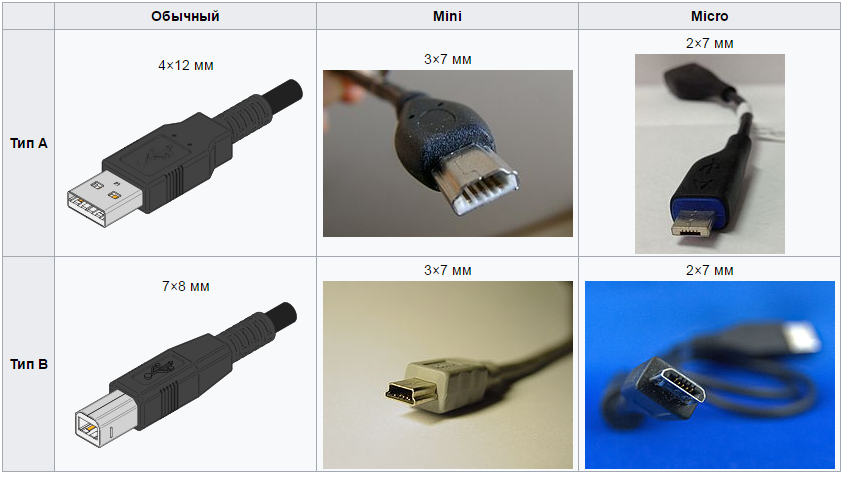
Распиновка штекера USB (обычный, mini, micro).
Виды разъёмов USB.
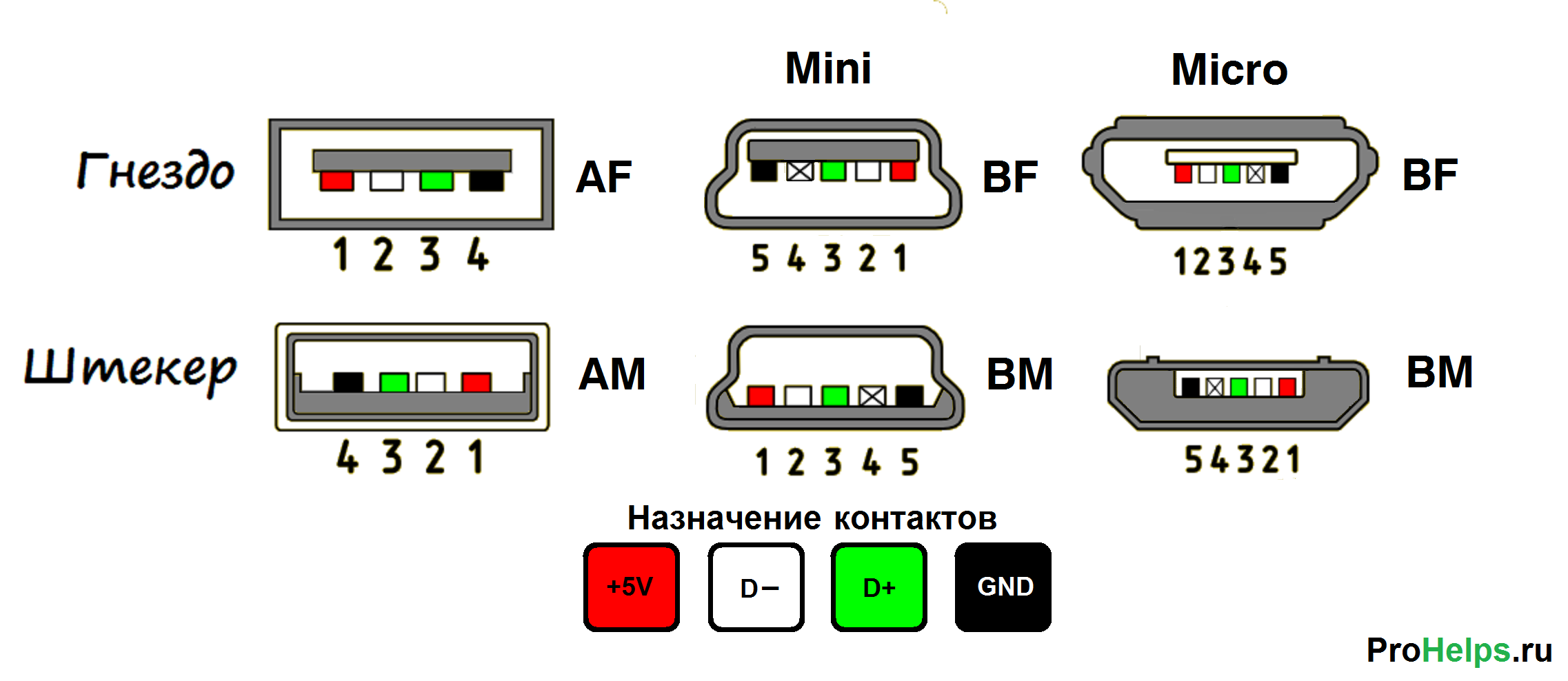
Распиновка usb кабеля по цветам.
Распиновка Usb 2.0.
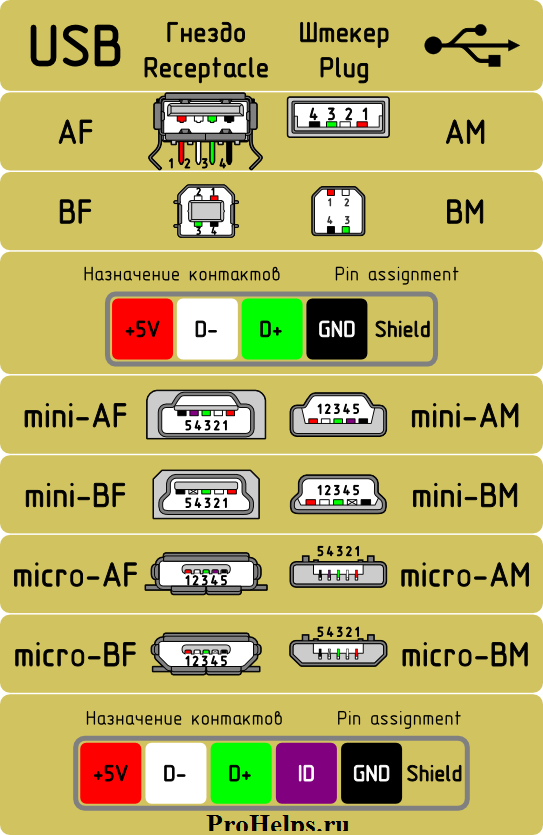
USB micro
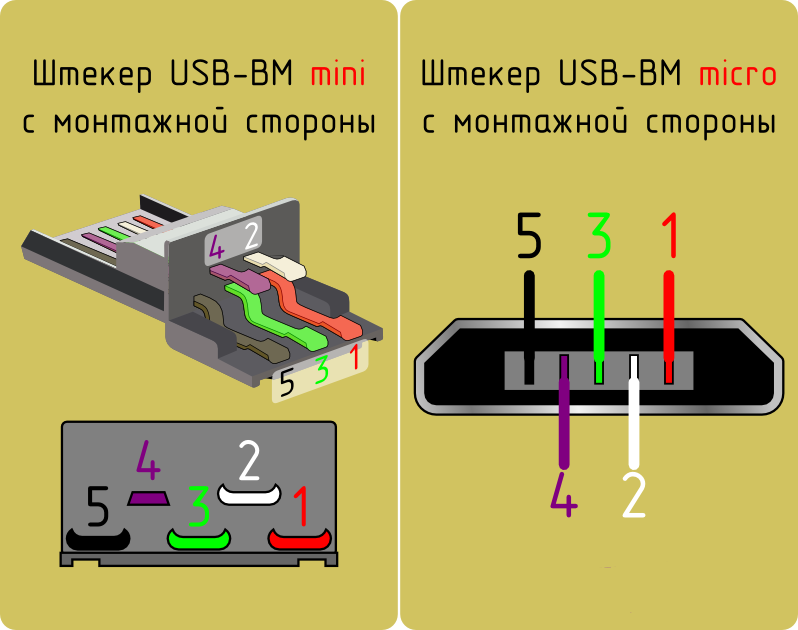
Видео.
интернет-магазин светодиодного освещения
Пн - Вс с 10:30 до 20:00
Санкт-Петербург, просп. Энгельса, 138, корп. 1, тк ''Стройдвор''








Поделиться с друзьями: